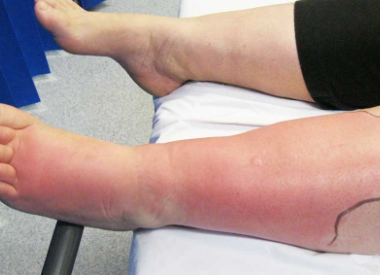
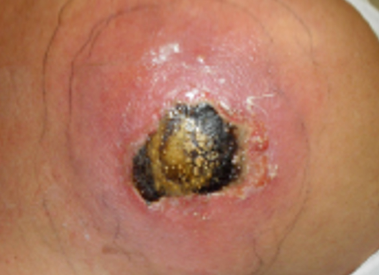
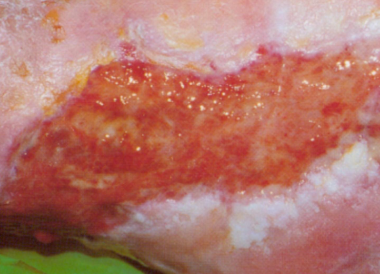
SSTIs can vary widely in presentation and etiology, and range in severity from mild infections, including uncomplicated abscess, to life-threatening necrotizing fasciitis.1,2 The exact presentation of SSTIs varies depending on the type of infection but generally includes redness, edema and/or induration around the site of the infection.1-4 Current SSTI treatment guidelines further distinguish between non-purulent infections (such as cellulitis) and purulent infections (such as cutaneous abscesses).1,5