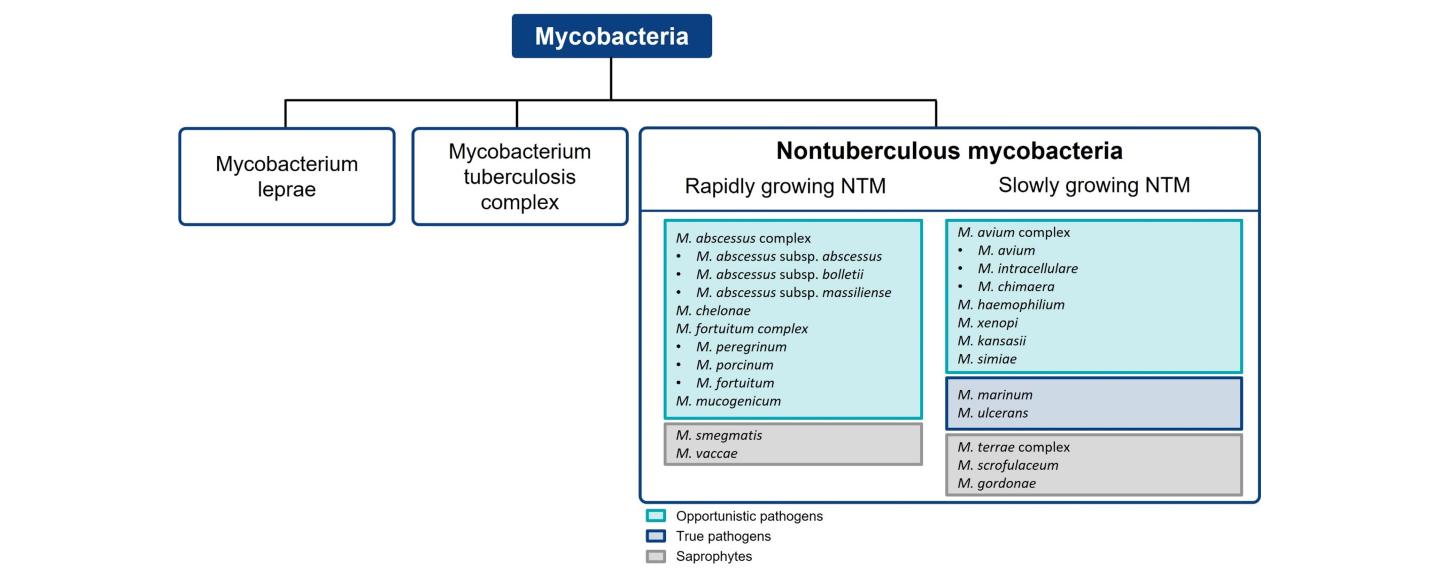
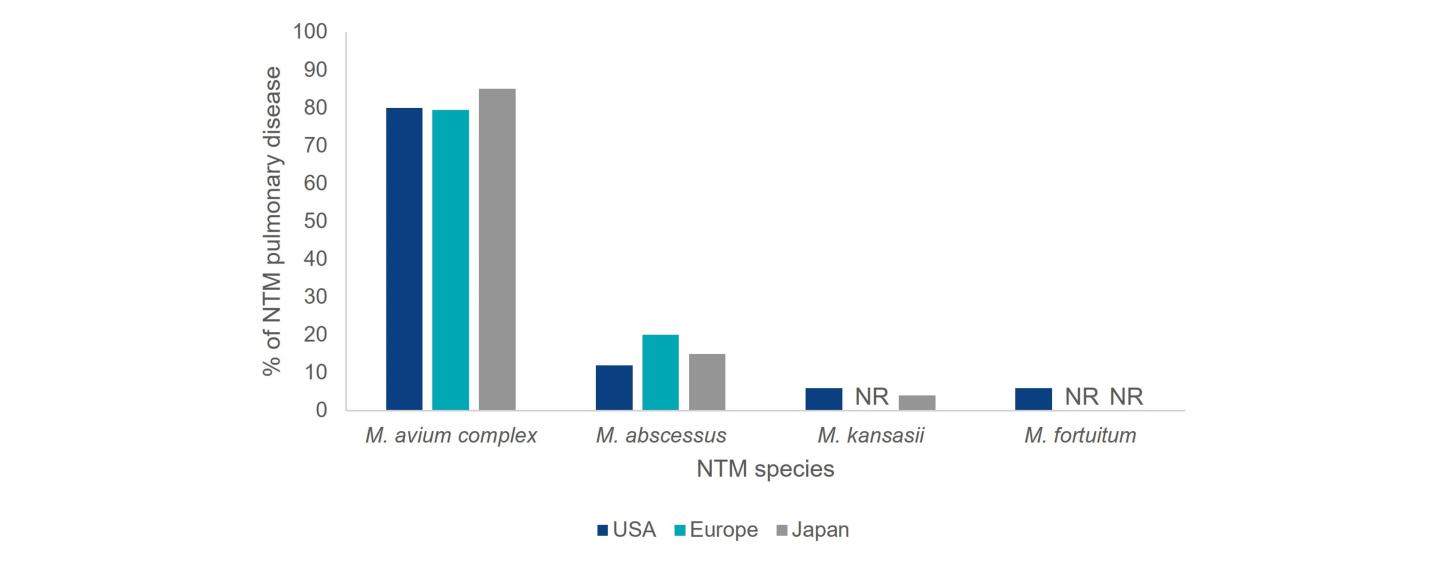
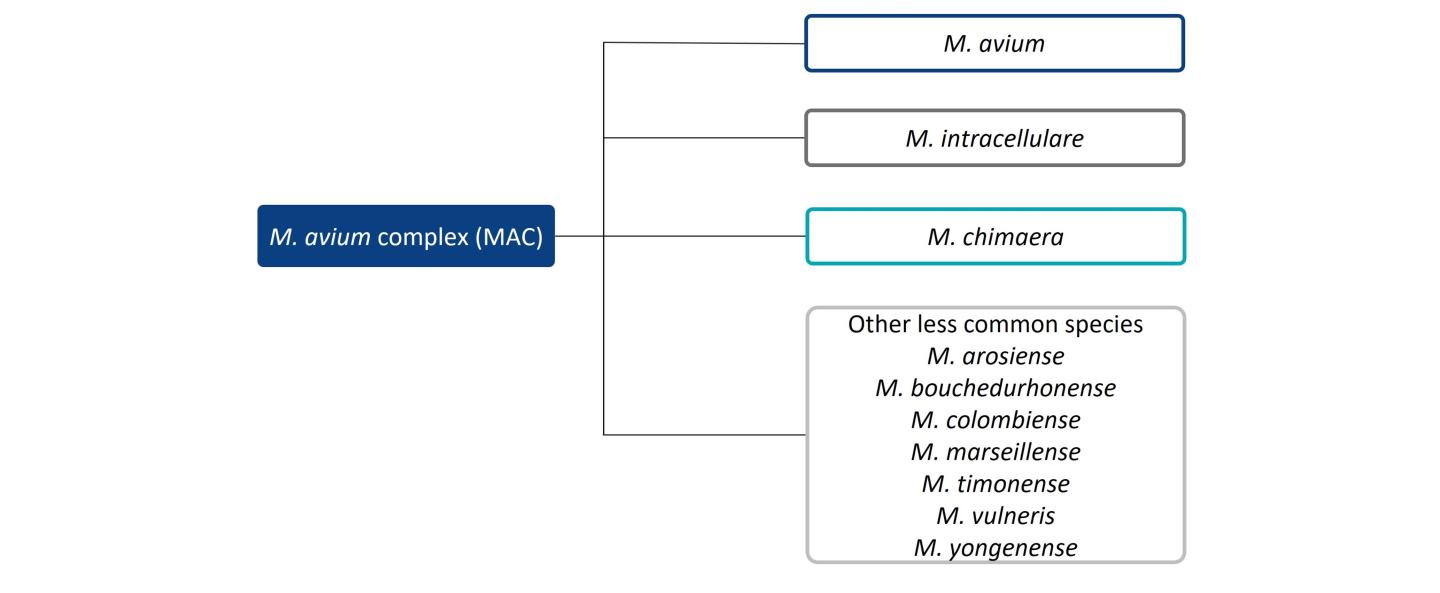
The distribution of NTM species causing pulmonary disease varies by geographic region.3 M. avium complex (MAC) and M. abscessus are responsible for the bulk of NTM pulmonary disease in the US, making up approximately 80.1% and 12.1% of cases, respectively.2 A survey on diagnostic and treatment practices for NTM pulmonary disease in five European countries (France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK) and Japan found that MAC predominated as the causative agent of NTM pulmonary disease (Europe: 79.4%; Japan: 85.1%), followed by M. abscessus (Europe: 20%; Japan: 14.9%).6